Personalized Stem Cell is an exciting area of medicine that holds great promise for the treatment of a wide range of medical conditions.
One promising source of stem cells is adipose tissue, which is the fat found in the body. This type of stem cell therapy is gaining popularity due to the abundance of stem cells that can be obtained from adipose tissue and the promising results seen in early studies. In this article, we will explore the potential benefits of stem cell therapy from adipose tissue and how it works.

What is Personalized Stem Cell Therapy?
Personalized stem cell therapy is a type of regenerative medicine that uses a patient’s own stem cells to promote healing and repair. The process begins with the extraction of stem cells from the patient’s adipose tissue, also known as fat tissue. Adipose tissue is a rich source of stem cells, which can be harvested through a minimally invasive procedure.
Once the stem cells are extracted, they are processed and prepared for injection into the patient’s damaged tissues or organs. Because the stem cells come from the patient’s own body, there is a reduced risk of rejection or adverse reactions.
Which parts of the body can stem cells be collected from?
Stem cells can be collected from various sources in the body, depending on the specific needs and purposes. Some of the common sources include:
- Adipose tissue: Adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) can be obtained from fat tissue. The collection process is relatively easy and safe, making them suitable for various therapeutic applications.
- Blood: Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) can be collected from blood. These stem cells have the ability to differentiate into various blood cells, such as red blood cells and white blood cells.
- Bone marrow: Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) can be collected from bone marrow. These stem cells can differentiate into various types of tissues, such as bone and muscle tissues.
- Umbilical cord blood: Another source of stem cells is the blood found in the umbilical cord after childbirth. These stem cells have properties similar to those of HSCs and can differentiate into various blood cells.
- Dental pulp: Dental pulp stem cells can be obtained from extracted teeth, particularly wisdom teeth. These stem cells have the potential to differentiate into various cell types, including bone, cartilage, and neural cells.
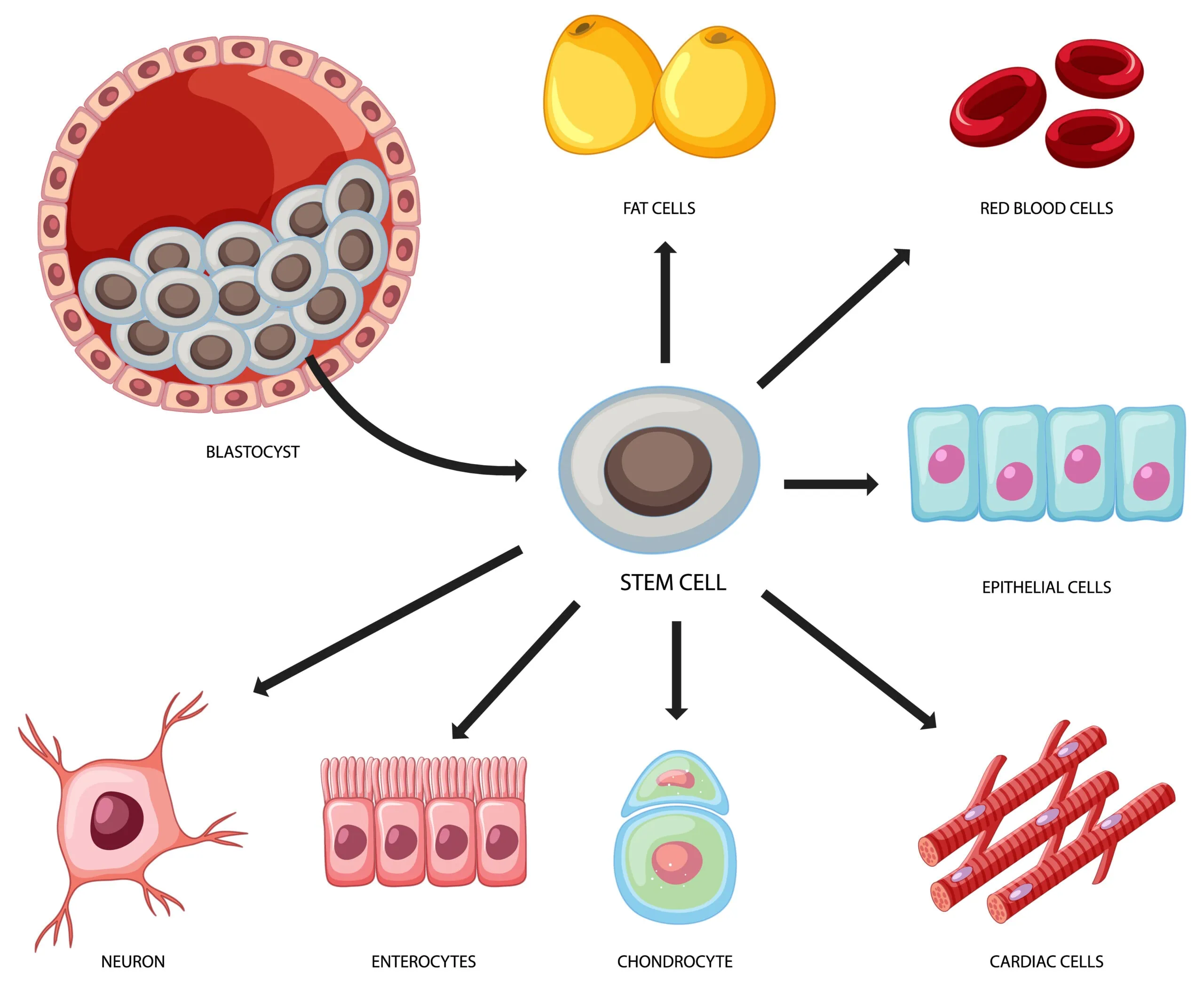
Types of stem cells
- Embryonic stem cells: These stem cells are derived from early-stage embryos and have the ability to differentiate into any cell type in the body. They are known as pluripotent stem cells, meaning they can give rise to any cell in the body. Embryonic stem cells have been the subject of much controversy due to ethical concerns related to their sourcing from human embryos.
- Adult stem cells: Also known as somatic stem cells, these stem cells are found in various tissues throughout the body, such as the bone marrow, blood, and brain. They have a more limited ability to differentiate into specific cell types than embryonic stem cells, and are known as multipotent stem cells. However, they still have important therapeutic potential and have been used in the treatment of a variety of conditions.
- Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs): These are adult stem cells that have been genetically reprogrammed to behave like embryonic stem cells, with the ability to differentiate into any cell type in the body. This technology has allowed researchers to bypass the ethical concerns surrounding the use of embryonic stem cells, and has opened up new avenues for research and potential therapies.
Benefits of Stem Cells
Stem cells offer numerous benefits to our bodies as they can differentiate into various cell types and have the ability to develop into other cells within the body. This is the reason why stem cells have the potential to regenerate tissues and cells in the body. Moreover, they have various medical and therapeutic applications, such as:
Body regeneration and disease treatment:
- Regenerating the body: Stem cells can differentiate into various cells in the body, which can be used to regenerate tissues or organs that are damaged, such as treating heart disease by regenerating damaged heart tissue or using stem cells to regenerate skin tissue after burns.
- Treating diseases: Stem cells can be used to treat various diseases, such as cancer, by using stem cells to help regenerate tissue damaged by radiation or chemotherapy. They can also be used to treat diabetes by creating new cells to replace damaged parts of the kidney.
- Reducing inflammation: Stem cells can produce various substances such as cytokines, growth factors, and anti-inflammatory factors that help reduce inflammation and regenerate tissues, making them suitable for those with inflammatory problems or other conditions resulting from inflammation.
Skin and beauty benefits:
- Rejuvenating and improving skin complexion: Stem cells can help regenerate and improve deteriorated skin cells, making the skin appear younger and more radiant.
- Reducing wrinkles: Stem cells can stimulate the production of collagen and elastin, which are the main components of the skin, making the skin stronger and reducing the appearance of wrinkles.
- Reducing dark spots and blemishes: Stem cells can reduce the production of dark pigment and stimulate the production of light pigment in the skin, making the skin appear more even and youthful.
- Nourishing and maintaining skin: Stem cells can help nourish and maintain healthy and strong skin by stimulating the production of complete and strong subcutaneous cells.
- Treating skin diseases: Stem cells can help treat skin diseases such as rashes, photosensitivity, and other skin conditions.
Stem Cell Collection from Adipose Tissue
Stem cell collection from adipose tissue is a process used to extract stem cells from the body’s fat tissue. Adipose tissue is a source of potent stem cells with the ability to grow and differentiate into other cell types. These stem cells are called “adipose-derived stem cells” (ADSCs) and are significant in medical research for their potential use in treating various diseases or for anti-aging purposes. The procedure is safe and does not pose risks of allergic reactions since the cells are derived from the patient’s own body.
Stem Cell Collection from Adipose Tissue Process
The process of collecting stem cells from adipose tissue at Siam Clinic Phuket consists of the following steps:
- Inform the staff of your interest and undergo a preliminary health examination.
Those who wish to collect stem cells should schedule a consultation with a doctor to learn about the benefits of storage for future use. After making a decision, there will be a check-up, blood test screening, cancer marker check, and evaluation of chronic health conditions. If all results are satisfactory, an appointment will be scheduled with the medical team for fat removal and stem cell culture in the laboratory.
- Perform liposuction to collect fat cells and culture them in the laboratory.
On the day of liposuction, the doctor will insert a small tube into the adipose tissue and use a vacuum device to extract fat from the desired area. For stem cell collection, only 10 cc of fat is required. Those who are already undergoing liposuction to remove excess fat from specific areas can also choose to collect fat cells for stem cell culture (Stem Cell) at the same time.
- Stem Cell Therapy
After collecting stem cells from fat and sending them to the laboratory for culture and storage in a stem cell bank, if you want to use them, you can inform Siam Clinic Phuket to prepare the appropriate number of cells for use. When collecting stem cells from adipose tissue, “they can be stored in a stem cell bank for up to 60 years.” Before using the stem cells, their quality and efficacy will be checked every time.

Stem Cell Bank
After the fat extraction process for collecting adipose-derived stem cells, the next step is to choose a reputable and highly standardized stem cell bank that operates professionally.
Siam Clinic Phuket collaborates with “Medeze Stem Cell” as we recognize the importance of storing your stem cells. We are dedicated to providing lifetime service for the cryopreservation of your stem cells.
“Medeze Stem Cell” differentiates itself from other stem cell banks that freeze tissues without checking and isolating them for further cell culture. At Medeze Stem Cell, we immediately examine both the quantity and quality of your stem cells. We also reserve at least 10 million stem cells in the long-term storage area for you. This means you will always have a personal reserve of stem cells available for future use.
Where is the best place to store Personalized Stem Cells?
When considering where to store personalized stem cells, several factors need to be taken into account, such as the credibility of the facility providing the storage services, the cleanliness and safety of the stem cell collection process, and the standard of the stem cell bank itself.
A good stem cell storage facility should be trustworthy, have a safe and sterile process for collecting personalized stem cells, and maintain high standards to ensure the most effective treatment and prevent potential errors.
In conclusion, it is crucial to conduct thorough research on the available facilities and stem cell banks before making a decision. Look for a facility with a strong reputation, strict safety measures, and a high standard for storing personalized stem cells to ensure the best possible outcome for your future treatments.
Interested in our service, contact us
- Map : https://g.page/SiamClinicPhuket
- Tel : 088-488-6718 และ 093-692-5999
- Email : [email protected]
- Facebook inbox : https://m.me/siamclinicthailand
- Instagram : https://www.instagram.com/siamclinic
- Line@ : https://lin.ee/uny1D7n